
SBG Systems announces the release of the first MEMS-based Gyroscope
A MEMS-based gyroscope for demanding underwater and geospatial applications.
In parallel with its OCEANS activity, CADDEN offers sensors and services with the ROBOTICS domain, focusing on 3D positioning, orientation measurement and optical remote sensing technologies. These solutions respond to multiple applications and are integrated into autonomous and industrial systems.
With the help of the constellations of positioning satellites (GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo), the GNSS receiver calculates coordinates of a position in the world, with sub-metric accuracy up to centimeters, in real time or in post-processing.
It comes in several forms: GNSS box with separate GNSS antenna, receiver and GNSS antenna in the same enclosure (also called «Smart Antenna»), GNSS compass with 2 antennas, GNSS OEM board.
Sometimes referred to as the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) or the Inertial Navigation System (INS), an inertial control unit is defined as a navigation system providing the orientation of a mobile in a 3D space.
Generally, there are two types of inertial centres: the inertial navigation centre with a GNSS receiver (internal or external); it is designed to obtain navigation and speed data in addition to orientation measurements.
If we want to obtain only the information of roll, pitch, yaw (and sometimes pilonement), it is better to choose an inertial center of heading or attitude.




The Lidar’s Remote Sensing And Ranging method is a laser sensor that collects measurements of the “flight time” (TOF or “Time-Of-Flight”) of light beams. The Lidar sensors calculate distances and light intensities very precisely to map a 3D environment.
Several types of Lidars correspond to the majority of applications: 2D Lidar, 3D Lidar, solid-state Lidar.
The technologies of GNSS receivers, inertial units and Lidar are used alone or in combination in various embedded systems.
For several decades, car manufacturers such as Renault, Tesla and Volvo have been working hard to become the pioneers in the autonomous transport market. After a long legal question, a decree published in July 2021 authorizes the use of autonomous cars on the French road network as of September 2022.
This no longer concerns only cars, but several solutions: buses, shuttles, robot taxis, etc. which are planned for the management of the «last mile delivery» (last mile delivery) or even improve mobility in certain rural areas.
Examples of use
In collaboration with FH Electronics, LAMIH unveiled a project in early 2022 related to “man-machine” cooperation, and more specifically on driving aids (adaptive cruise control, unintentional line crossing warning, sign recognition, etc.).
The two organizations developed a prototype “Cooperative Vehicle” based on a DS7 (Stellantis) with a Lidar Hesai XT32 distributed by CADDEN on its roof. The objective of this prototype is to test, in real life, the developments carried out beforehand in the SHERPA driving simulator, in service since 1997.
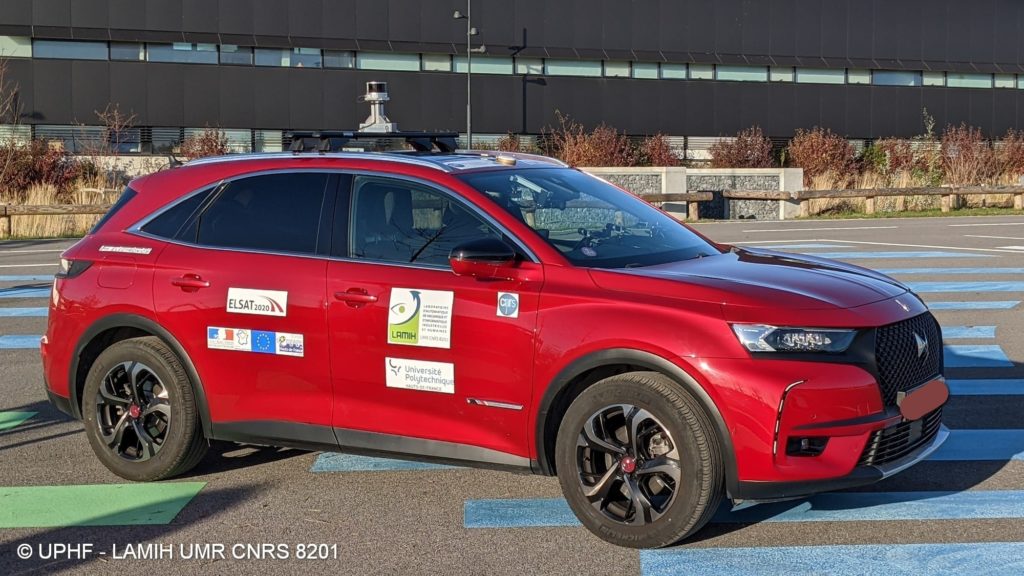
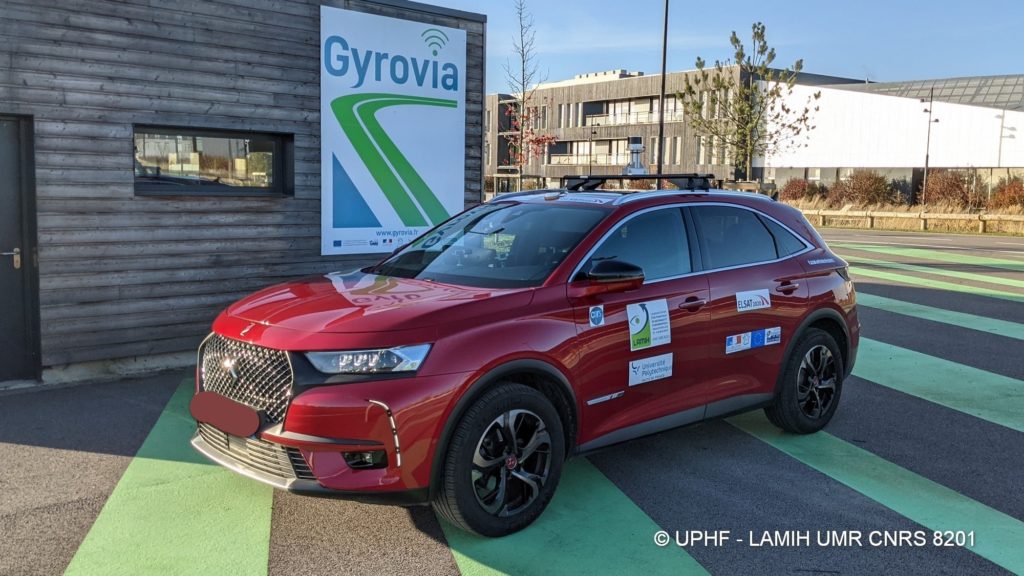


The Stellantis vehicle was developed as part of the ELSAT2020 project. It was co-financed by the European Union with the European Regional Development Fund, the State and the Hauts-de-France Region.
The LAMIH (Laboratoire d’Automatique, de Mécanique et d’Informatique Industrielles et Humaines) is a joint research unit between the Université Polytechnique Hauts de France (UPHF) and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS).
In 2021, the American company Nuro partnered with the giant Domino’s to design an autonomous delivery vehicle, equipped with a Hesai Lidar, model Pandar40, on its roof, programmed to deliver its pizzas in several states of the United States.
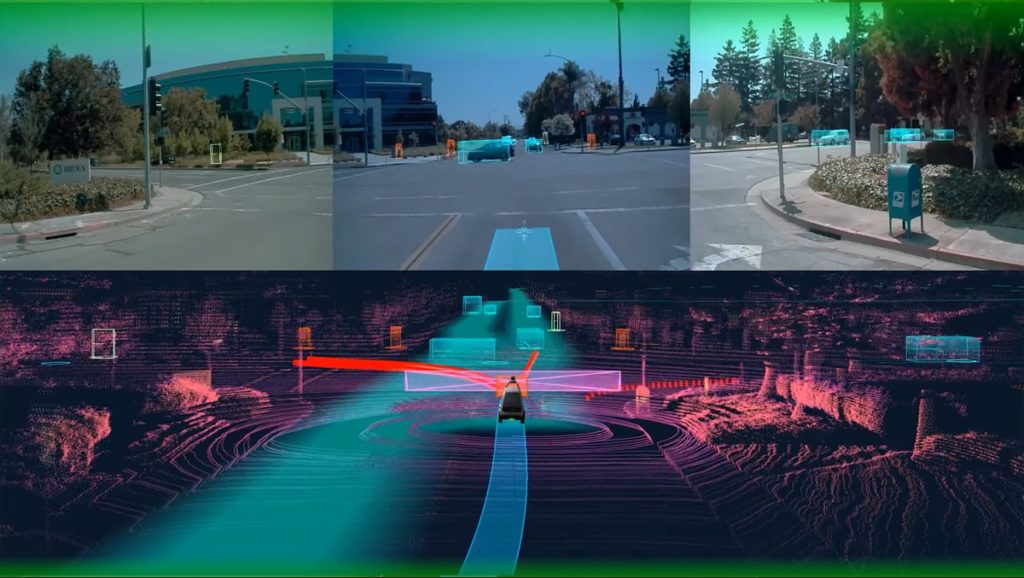

In 2018, the French company Navya experimented for a month an autonomous shuttle within the city of Nantes as part of Nantes City Lab. A first for the city that provisionally equipped itself with a self-driving, clean-energy vehicle (although in this test, an agent was in all vehicles) where a Velodyne Lidar laser sensor distributed by CADDEN was installed at the front of its roof.

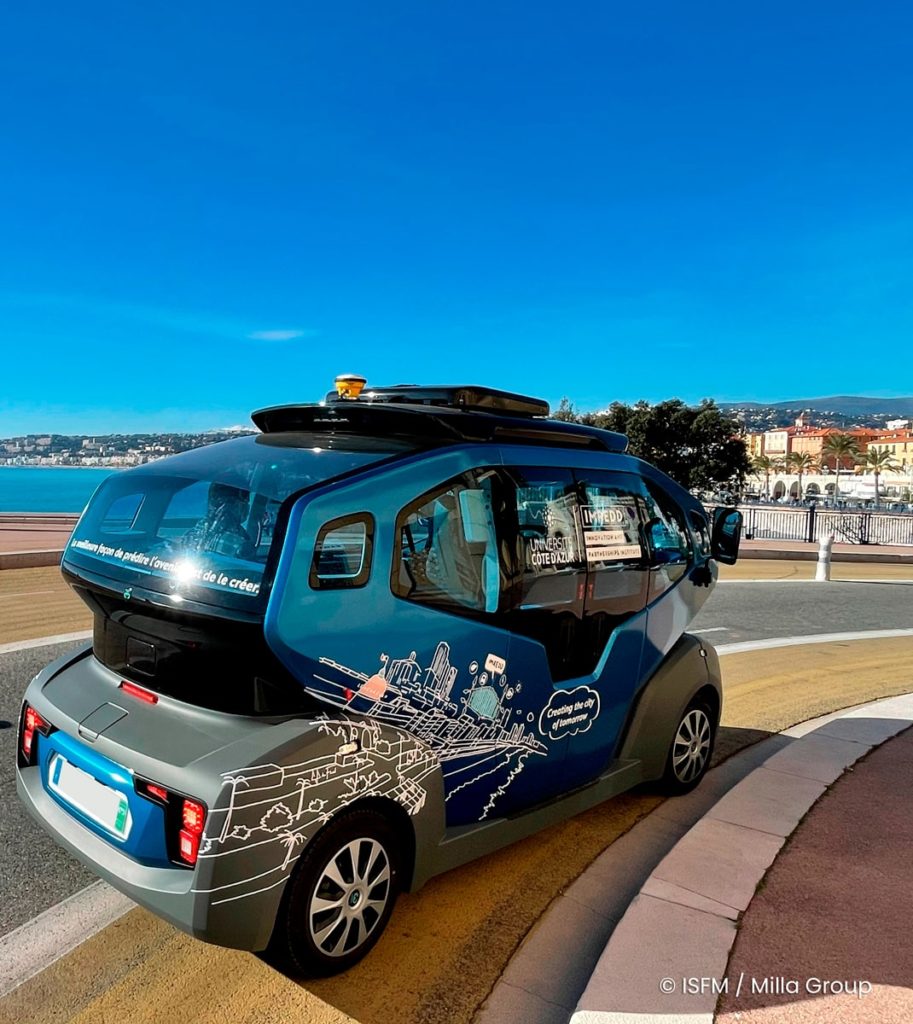
The French company Milla tested its autonomous shuttle called «Milla Pod» in January 2021 in the streets of Nice. Equipped with GNSS antennas from the manufacturer Trimble and supplied by CADDEN, it complements an already existing mobility offer in Nice. Users will be able to use it for short journeys to reach a tram stop for example.

These different technologies are integrated into autonomous machines specialized in the automation of logistics tasks. These are autonomous freight vehicles, AGVs (“Autonomous Guided Vehicle”), AGVs (“Autonomous Mobiles Robots”), container trucks, valet robots and pallet trucks used to assist operators in logistics and automate the simplest tasks.
More concretely, they navigate warehouses, detect racking, place or drop packages and pallets, etc. in a wide variety of environments (food warehouse, hospital or factory).
Examples of use
Stanley Robotics presents the «Stan» valet parking robot, equipped with a Velodyne Lidar provided by CADDEN to optimize the parking space on the car parks. The objective is to free users from the worries related to the management of their vehicle during their absence.
First real-life tests were carried out in 2017 on long-term airport car parks, indoors in Roissy-Charles de Gaulle (Paris), then outdoors – a “world first” for this type of system – in Lyon Saint-Exupéry.

Autonomous tractors are being used in agriculture to perform complex tasks, such as maintaining agricultural and wine plots or responding to labour shortages.
Examples of use
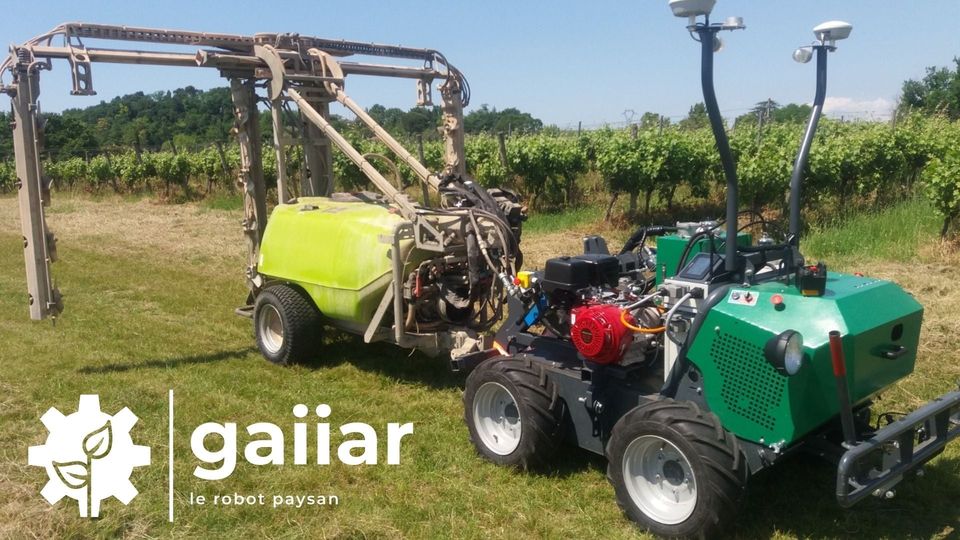
The farmer robot Gaiiar is equipped with two GNSS Trimble Intech antennas distributed by CADDEN, allowing it to evolve among wineries. This solution meets the demand for automation of tasks on the part of the operators as well as the shortage of labour in the sector.
In some cases, the robot completely replaces the tractor since it can be coupled with a sprayer and thus protect the user during spraying. The goal is to limit fuel consumption while adjusting the speeds and mass of the unit.

The characteristics of the Lidar technology make it a real asset in the context of environmental monitoring and safety. This sensor meets the multiple needs of intrusion detection of people or flying drones even in bad weather, gauge measurement and anticollision assistance system.
Examples of use
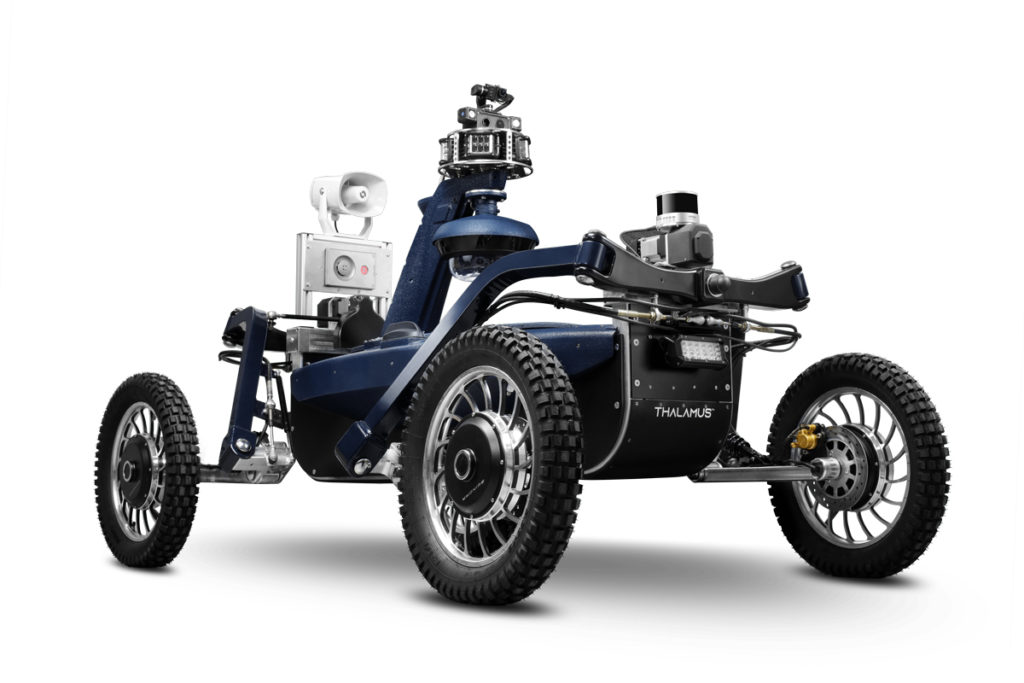
The manufacturer Glocal Robotics offers its robot named Thalamus, equipped with Lidar of the manufacturer Hesai, model XT32 provided by CADDEN, and designed to ensure the surveillance of sensitive sites.
After several tests, the robot has been evolving since 2022 in environments that are difficult to monitor permanently with guards or cameras (large military and industrial infrastructures, very large sites, etc.).

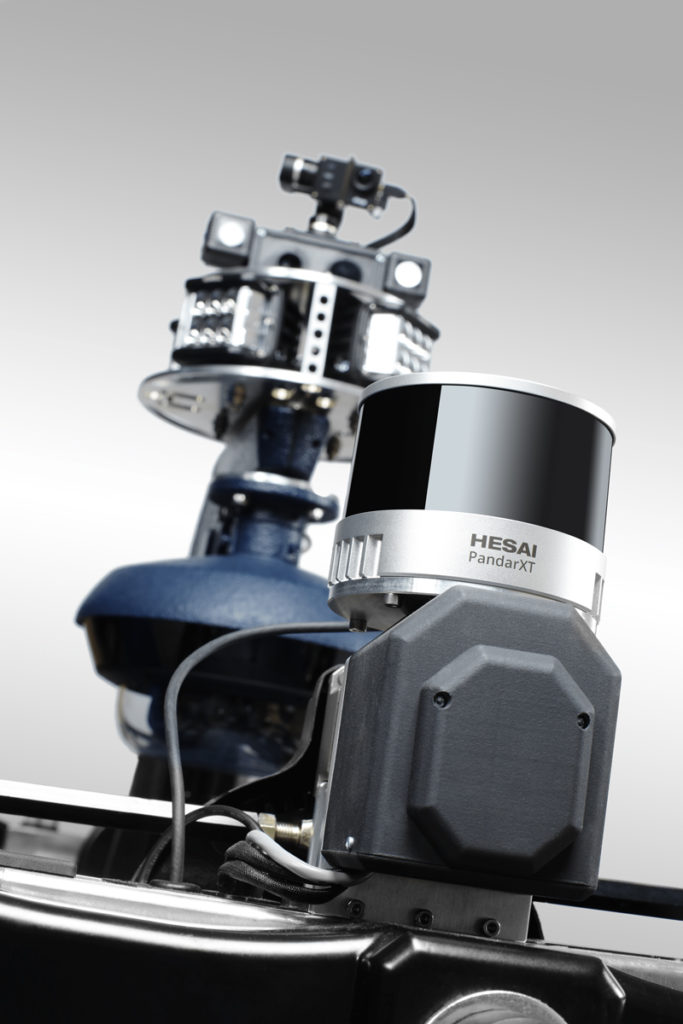
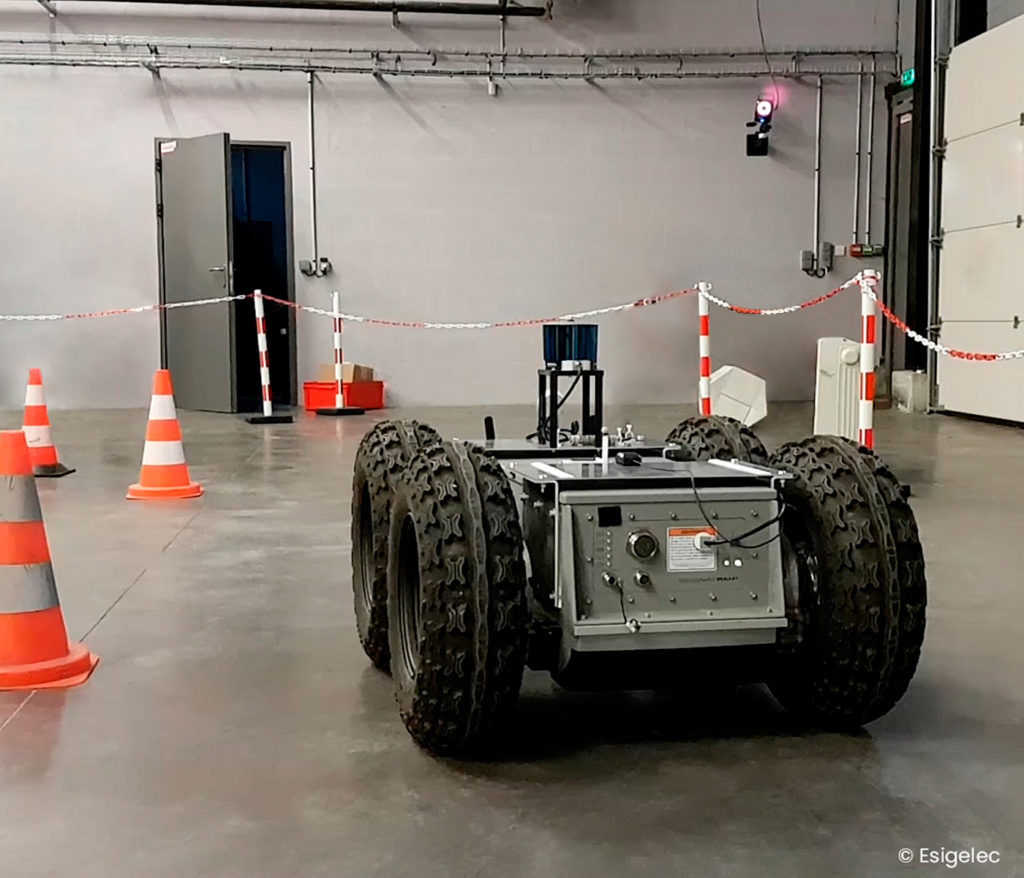
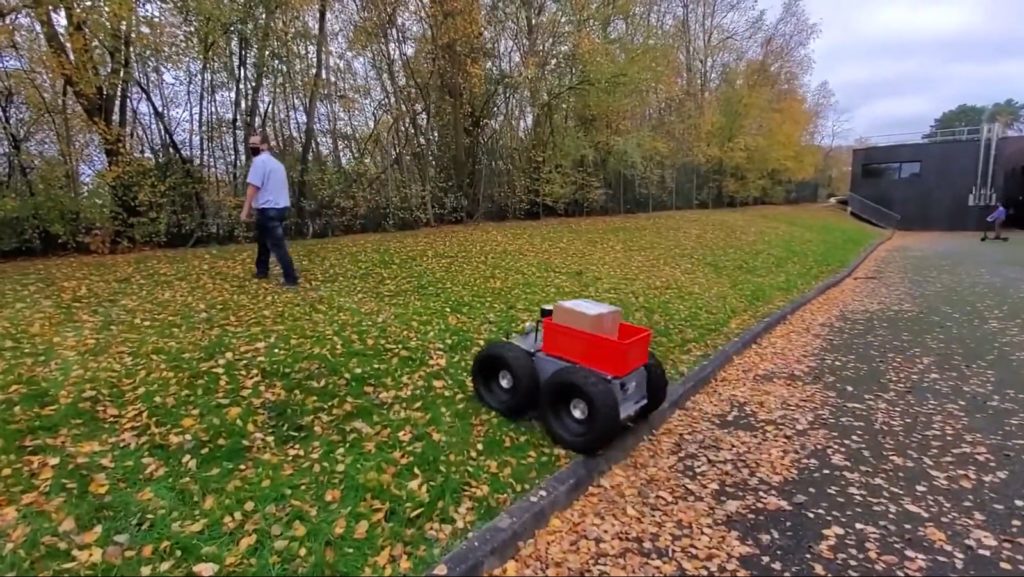
The engineering school has developed a robot called «Jean-Michel», equiped with a Hesai Lidar supplied by CADDEN, which carries out various outdoor exploration missions: parcel delivery, measurement of a distance travelled regardless of the terrain, followed by a target, etc.


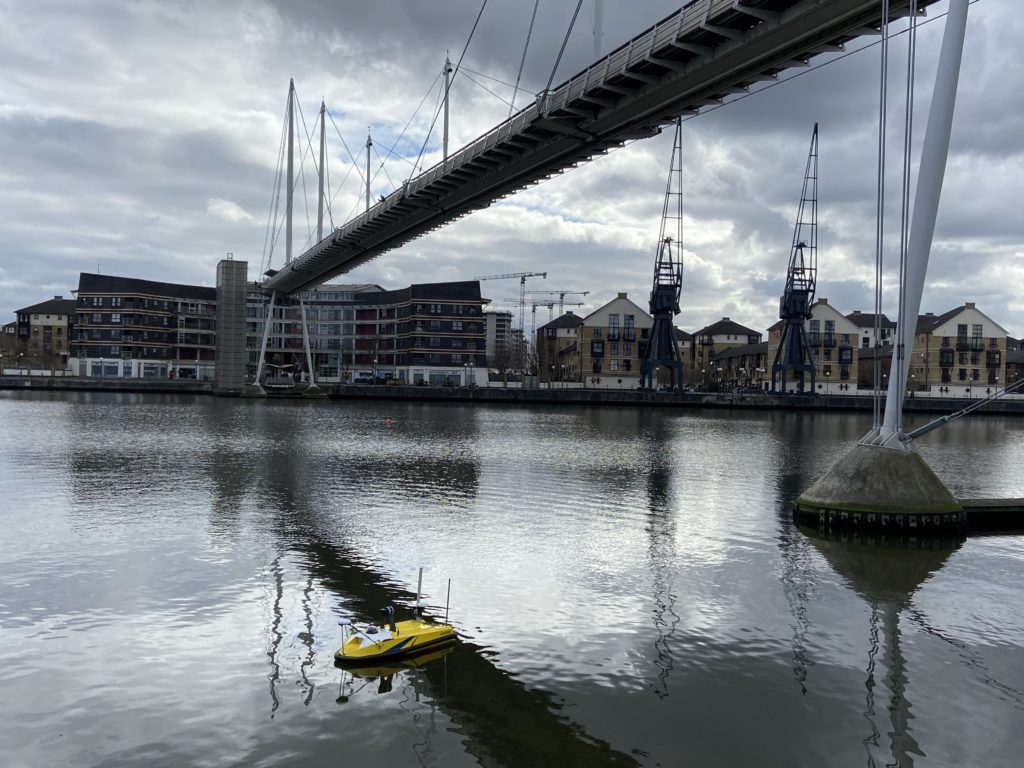
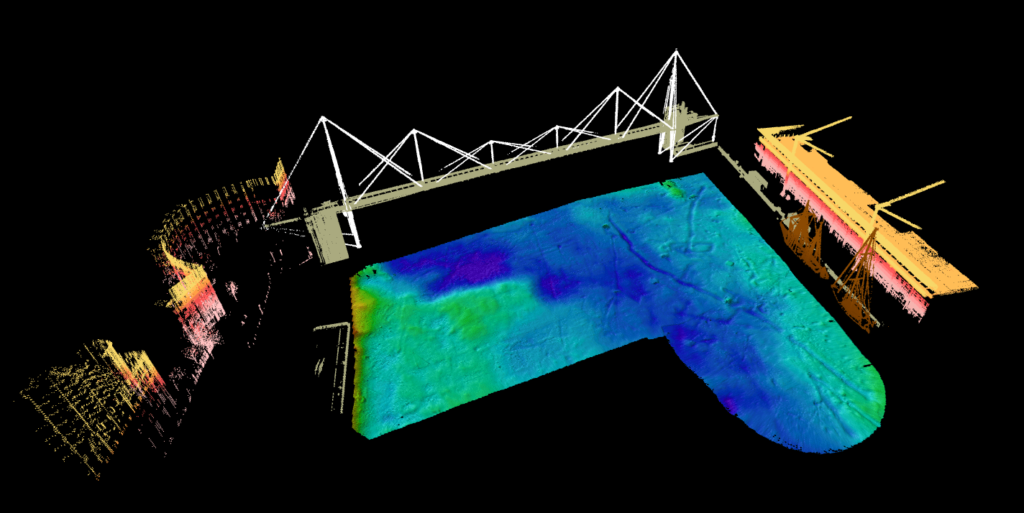
All ROBOTICS technologies are combined for the applications of hydrography and more particularly bathymetry in various environments (inland, coastal or high seas).
Examples of use
USV dedicated to hydrographic applications, including bathymetry, are equipped with Lidar in addition to GNSS receivers, inertial power plants and beam sounders. The objective is to capture the environment below and above water level (bridges, banks, buildings, etc.) in a single passage.

Did you like this article ?
Share it with your colleagues or friends
Read next

A MEMS-based gyroscope for demanding underwater and geospatial applications.

The new ultra-compact Sprint-Nav U for integration on UAVs, ROVs and USVs

An event packed with conferences, workshops and celebrations!

Tous droits réservés – 2024
Vos données sont collectées et traitées pour vous envoyer notre newsletter et améliorer l’expérience utilisateur du site web. Dans ce cadre, le responsable du traitement est CADDEN. Vous disposez d’un droit d’accès, de rectification, et de suppression de vos données, ainsi que d’un droit de limitation, de portabilité ou d’opposition. Pour exercer ces droits, vous pouvez nous contacter via le formulaire de contact. Pour plus d’informations sur la façon dont nous traitons vos données personnelles, vous pouvez consulter notre Politique de confidentialité.